What is an ankle sprain?
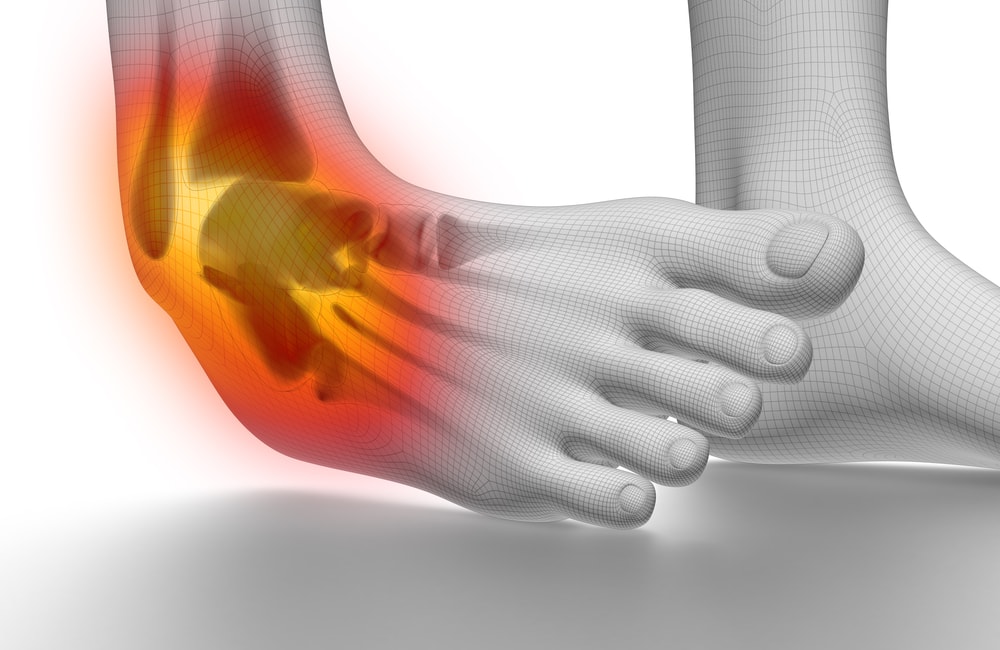
An ankle sprain is a wound to the hard crews of tissue (tendons) that mount and connect the bones of the limb to the foot. The injury all about ankle sprains usually occurs when you by accident turn or difficultly crack your ankle. This can be expanse or split the tendons that hold your ankle bones and joints together.
Things to know about an ankle injury
The entire tendons have a wide range of motion and margins that enable them to keep the joints alleviated. When ligaments surrounding the ankle are hard-pressed past these margins, it causes a twist. Sprained ankles most normally encompass injuries to the tendons on the external of the ankle.
What causes an ankle sprain?
An ankle sprain always happens when the base abruptly screws or rolls, forcing the ankle joint out of its regular point. However, physical activity should be performed; the ankle can turn inward hence due to abrupt or unpredicted movement. This causes one or more tendons around the ankle to give or tear.
Ankle sprains can occur to anybody at any age. Involving in sports, walking on rough surfaces, or even wearing inappropriate footwear can all cause this kind of injury.
What are the symptoms of an ankle sprain?
You might have an injured ankle if you observe the following signs in the ankle:
- swelling
- tenderness
- bruising
- pain
- inability to put weight on the affected ankle
- skin discoloration
- stiffness
The ankle can sustain several distinct types of wounds. It’s significant to see your specialist when you’re going through complications with your ankle. Your specialist can control whether the injury is a sprain or something more serious.
How is an ankle sprain diagnosed?
Dr. Dhananjay Gupta is one of the top orthopedic specialists and will do a physical test to regulate which tendons have been torn. All through the test, your surgeon may move your ankle joint in different ways to check your wide-ranging of motion.
Imaging tests, like X-rays, can also be ordered to consider a bone breakage. An MRI can be done if your surgeon doubts a fissure, a severe injury to the tendons, or fracture to the surface of the ankle joint. The MRI exam makes use of a robust magnetic area and radio waves to build thorough images of the body. This enables your specialist to provide an accurate diagnosis.
How is an ankle sprain treated?
When treating a wrenched ankle that may lead to retrieval and combat against sprain and distress. It’s vital not to put weight on the wounded area although you’re recuperating from an ankle sprain.
Dr. Dhananjay will advise you to stay off of your bruised ankle unless the pain diminishes. For minor sprains, this can take a week to 10 days. However, more severe injuries can typically choose several weeks to cure.